Basic Grammar and Style in Technical Writing

Introduction
Clear and concise grammar is the backbone of effective technical writing. Proper grammar and a consistent style ensure that readers can easily follow your content without getting distracted by confusing wording or inconsistent phrasing. This blog post will cover essential grammar rules, the importance of style consistency, and practical tips to help you write with clarity and precision.

Why Grammar and Style Matter in Technical Writing
While grammar and style are important in any type of writing, they are especially crucial in technical writing, where the primary goal is to communicate complex information clearly. Errors in grammar or style can mislead readers, damage credibility, and lead to misunderstandings.
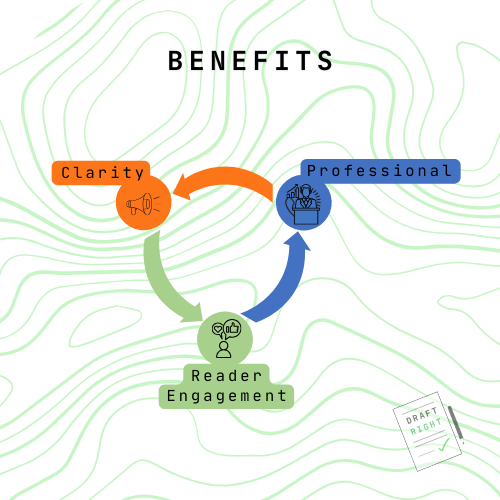
Benefits of Good Grammar and Consistent Style:
-
Clarity: Helps readers understand the information without second-guessing the meaning.
-
Professionalism: Well-structured sentences and a consistent tone create a polished and professional impression.
-
Reader Engagement: Smooth, error-free language keeps readers focused on the content rather than the writing itself.
Key Grammar Rules for Technical Writers
Let’s go over some essential grammar rules every technical writer should follow:
1. Use Active Voice
In technical writing, active voice is usually preferred because it’s direct and clear. Passive voice can make sentences wordy and harder to understand.
Example:
-
Passive Voice: “The device was configured by the user.”
-
Active Voice: “The user configured the device.”
2. Be Concise
Technical writing values brevity. Eliminate unnecessary words and phrases that don’t add meaning to your sentences.
Example:
-
Wordy: “Due to the fact that…” → Concise: “Because…”
-
Wordy: “In order to…” → Concise: “To…”
3. Avoid Ambiguity
Technical documents should never leave readers guessing. Make sure each sentence clearly conveys its intended meaning.
Example:
-
Ambiguous: “Turn it off after starting.”
-
Clear: “After starting the engine, turn off the auxiliary power.”
4. Use Consistent Terminology
Using consistent terms throughout your document helps readers follow along without confusion. If you start by referring to “the application,” don’t switch to “the app” or “the software” later unless absolutely necessary.
Image Prompt: Consider a visual showing an example of active vs. passive voice, with a checkmark next to the active sentence to reinforce best practice.
Essential Style Tips for Technical Writers
Style consistency is just as important as good grammar in technical writing. Style choices cover everything from tone and formatting to terminology and document structure.
1. Define Your Tone
Tone in technical writing should generally be neutral, informative, and supportive. Avoid being too casual or too formal; the goal is to sound helpful and professional.
Example:
-
Neutral Tone: “To begin, select ‘File’ and click ‘New Project.’”
-
Too Casual: “Let’s get started by opening a new project, just click on ‘File.’”
2. Use Plain Language
Plain language is crucial for technical writing, especially for beginner audiences. Opt for simple, straightforward words over complex ones.
Example:
-
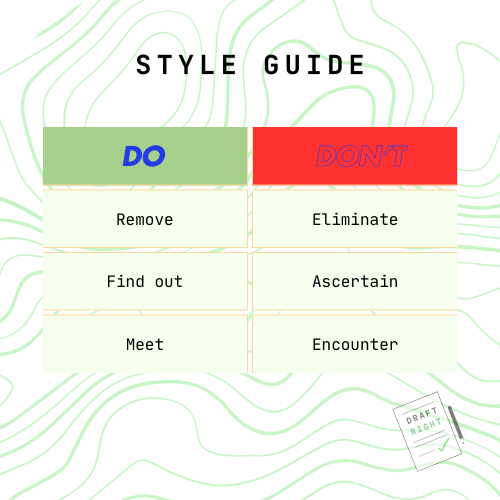
Use “use” instead of “utilize.”
-
Use “help” instead of “facilitate.”
3. Be Mindful of Formatting
Readable formatting can significantly improve comprehension. Use bullet points, numbered lists, and headings to organize information and make it easy to scan.
Example:
- Instead of writing out a process in paragraph form, use a numbered list for step-by-step instructions.
4. Follow a Style Guide
Many organizations and fields have their own style guides, such as the Microsoft Style Guide or the Apple Style Guide, to maintain consistency in technical writing. Following a style guide ensures that all documents have a similar look, feel, and structure.
Common Grammar and Style Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the basics is essential, but knowing common mistakes will help you refine your writing even further. Here are a few pitfalls to watch out for:
-
Overuse of Technical Jargon: Avoid heavy jargon, especially for a non-technical audience. Use technical terms only when necessary, and provide clear explanations if they might be unfamiliar to readers.
-
Inconsistent Formatting: If one section uses bullet points and another uses dashes for lists, it can be distracting and unprofessional. Stick to a consistent format.
-
Misplaced Modifiers: A modifier that’s too far from the word it describes can confuse readers. Place modifiers close to the word they modify for clarity.
Example:
-
Unclear: “The program crashed when trying to open the user.”
-
Clear: “When trying to open, the program crashed on the user’s request.”
Practical Tips for Improving Grammar and Style
Here are some actionable steps to refine your grammar and style:
-
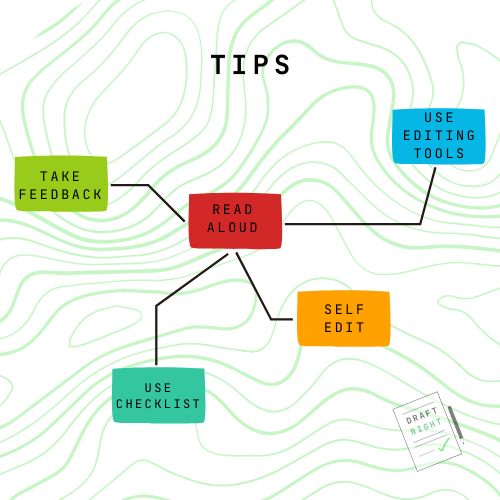
Read Aloud: Reading your work aloud can help you catch awkward phrasing or unclear sentences.
-
Use Editing Tools: Tools like Grammarly or Hemingway can help identify grammar issues and suggest improvements for conciseness and readability.
-
Practice Self-Editing: Step away from your document and come back with fresh eyes to edit. This can help you spot errors you may have missed initially.
-
Ask for Feedback: Share your document with colleagues or a peer for constructive feedback. They might spot grammar inconsistencies or style issues you missed.
Conclusion
Mastering grammar and style is crucial for effective technical writing. By following these essential grammar rules and adopting a consistent, clear style, you’ll produce documents that are not only correct but also easy to read and understand. As you move forward, remember that every choice you make in grammar and style directly impacts how well your audience receives and understands your message.