Crafting Clear and Concise Technical Writing

Clear and concise technical writing is the backbone of effective communication. It ensures that your audience can understand and act on the information provided without confusion or misinterpretation. However, achieving this clarity is often easier said than done. In this blog, we’ll explore proven techniques to make your technical writing concise and crystal-clear while maintaining its depth and accuracy.

Why Clarity and Conciseness Matter
- Improves Usability: Easy-to-understand content empowers users to achieve their goals quickly.
- Saves Time: Both writers and readers benefit from avoiding unnecessary verbosity.
- Enhances Credibility: Well-written documentation builds trust in your expertise.
Strategies for Crafting Clear Technical Writing
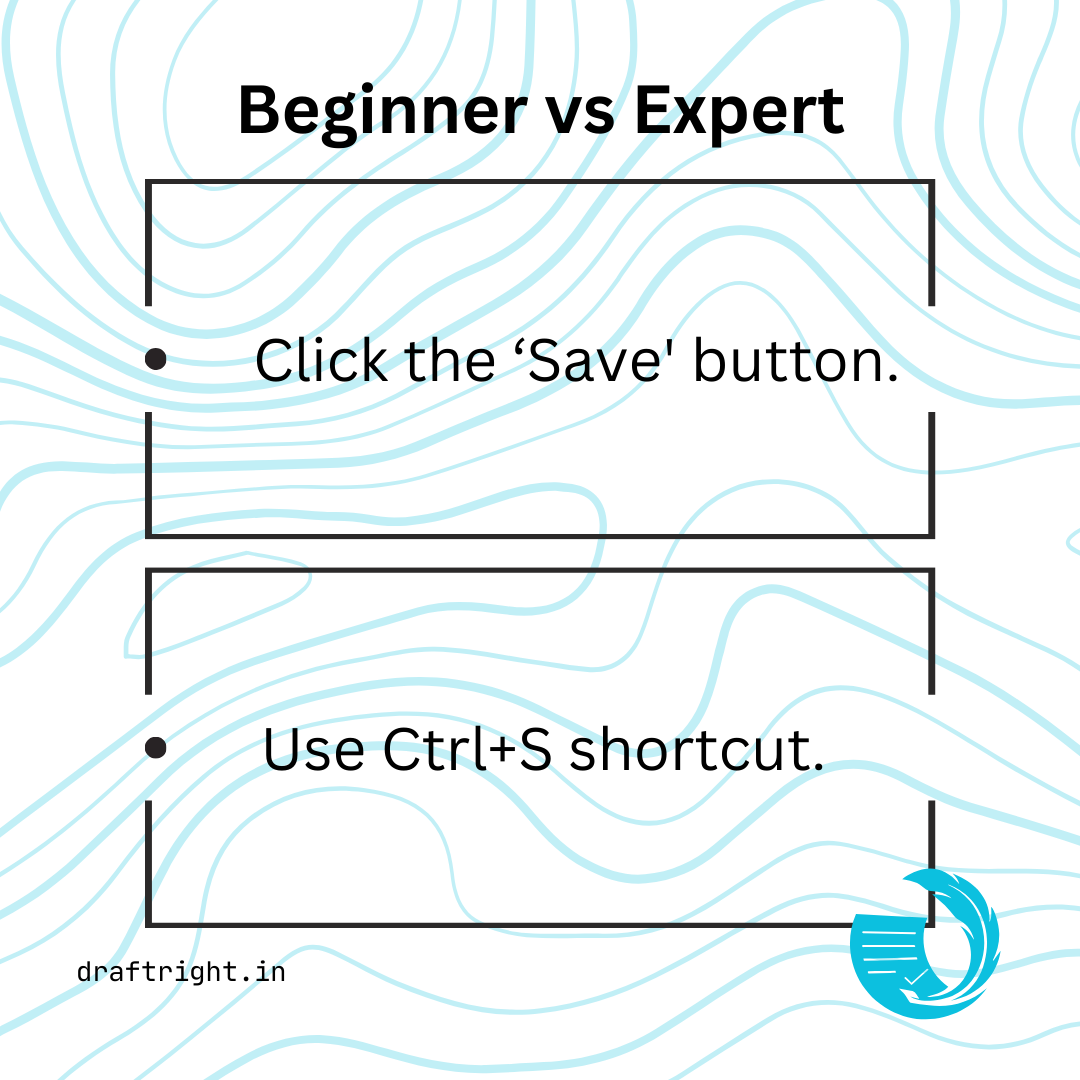
1. Know Your Purpose and Audience
Before you write, identify:
- The purpose of the document: Are you instructing, informing, or explaining?
- The audience’s expertise level: Use language and examples that match their knowledge.
Example:
- For a beginner: “Click the ‘Save’ button to store your document.”
- For an expert: “Save your document using the ‘Ctrl+S’ shortcut.”
2. Use Simple and Direct Language
Avoid complex words and phrases when simpler alternatives exist.
Examples:
- Instead of: “Facilitate the functionality of the apparatus.”
-
Write: “Enable the device.”
- Instead of: “Subsequent to completing the installation procedure…”
- Write: “After installing…”
3. Cut Out Redundancy
Avoid repeating ideas or using filler words that don’t add value.
Example:
- Instead of: “The user should always remember to back up their data before proceeding with the installation process.”
- Write: “Back up your data before installation.”

4. Focus on Active Voice
Active voice is more direct and engaging than passive voice.
Example:
- Instead of: “The settings can be changed by the user.”
- Write: “You can change the settings.”

5. Break Down Complex Ideas
When explaining complex processes, break them into smaller, manageable steps. Use numbered lists or bullet points for clarity.
Example:
- Open the settings menu.
- Navigate to “System Preferences.”
- Select “Network Settings.”
6. Leverage Visual Aids
Visual elements like charts, diagrams, and screenshots can reduce the need for lengthy explanations.
- Use screenshots to clarify software instructions.
- Include diagrams to explain hardware assembly.
- Ensure all visuals are labeled and referenced in the text.
7. Use Formatting to Enhance Readability
Readers should be able to skim your content and still grasp the main points.
- Use bold for emphasis.
- Highlight key terms with italics or colors.
- Include headings, subheadings, and bulleted lists.
8. Test Your Content
Share your writing with someone from your target audience and ask:
- Was the content clear?
- Were the instructions easy to follow?
- Did anything feel unnecessary or repetitive?
Incorporate their feedback to refine your document.

Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Using Jargon Excessively: Define or avoid terms your audience may not know.
- Writing for Yourself: Always focus on the reader’s needs.
- Overloading with Information: Include only what’s relevant and actionable.
Conclusion
Crafting clear and concise technical writing isn’t just about writing less—it’s about writing better. By prioritizing your audience’s needs and focusing on simplicity, structure, and readability, you’ll create documents that are not only informative but also enjoyable to read. Remember: great technical writing bridges the gap between complexity and comprehension.